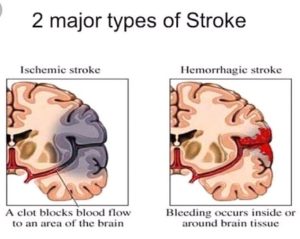
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die in minutes. A stroke is a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial. Early action can reduce brain damage and other complications. Most strokes are caused by an abrupt blockage of arteries leading to the brain (ischemic stroke). Other strokes are caused by bleeding into brain tissue when a blood vessel bursts (haemorrhagic stroke). Because stroke occurs rapidly and requires immediate treatment, stroke is also called a brain attack. The effects of a stroke depend on which part of the brain is injured, and how severely it is injured. Strokes may cause sudden weakness, loss of sensation, or difficulty with speaking, seeing, or walking.
Stroke is one of the leading causes of disability and death. About 60% of people survive a stroke but are left severely crippled. At an average of 250/100000 population there are about 25 million disabled people due to stroke in India.
Post stroke rehabilitation is a very important part of stoke management. Stroke usually causes paralysis with spasticity (stiffness) of one side of the body. Spasticity is a disruption in muscle movement patterns that causes certain muscles to contract all at once when you try to move or even at rest. The muscles remain contracted and resist being stretched. It interferes with movement and can also affect your speech and gait (walk). Spasticity can vary greatly; it may be as mild as the feeling of tightness of your muscles or may be so severe that it causes painful, uncontrollable stiffness and spasms of your extremities (flexor spasms). People with hand stiffness may have difficulty in using the hand crippling the hand especially if the right hand is involved. All muscles have some tone to maintain function, for example, activation of antigravity muscles to maintain sitting or standing postures. In an individual with spasticity, there is a velocity-dependent increase in muscle tone to passive movement. This creates an inability to stretch muscles or coordinate movements effectively. This stiffness or spasticity affects physiotherapy which is a very very important part of stroke rehabilitation. For mild cases of spasticity, physiotherapy and stretching exercises are usually very effective. But in severe spasticity, physiotherapy is least effective and usually very painful so that patient refuses to cooperate.
The drug used to treat spasticity is baclofen. Baclofen is a muscle relaxant and antispasticity drug. But the main problem is that it is not absorbed well in the stomach and also does not cross very well into the brain. Also it causes severe drowsiness and weakness in most patients as side effects.
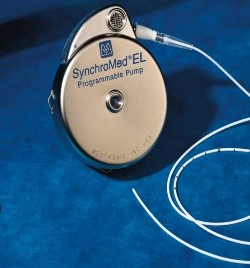
The brain and spinal cord is bathed in a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). So if any drug is put at the lower back, it can travel to the brain. This principle is used in cases of intrathecal drug delivery systems. The direct infusion into the intrathecal space minimizes the amount of drug needed to be effective. Limits or eliminates the common undesirable side effects associated with taking oral medications for spasticity. It can deliver a precise and consistent and continuous drug dose throughout the day, so as to avoid the peaks and valleys of taking oral medication. Also the dosing is very flexible and can be programmed as needed.
Before the surgery always a trial procedure is done on an OPD basis. Here 1 ml of baclofen is put into the CSF through a lumbar puncture and the effects as well as side effects are noted. If the effects are good and there are no side effects, then surgery will benefit the patient. In patients with stroke this will reduce the stiffness of the affected hands and legs.
This surgery is approved by various international agencies and in India by the CGHS, ESI etc. The pump has a capacity of 40 ml and can be refilled as an OPD procedure. This is usually once or twice ayear depending on the dose of drug required. There are usually not much complications of surgery except the usual infection, bleeding and hardware issues. However abruptly stopping the drug is dangerous and so patient has to be very prompt in refilling.
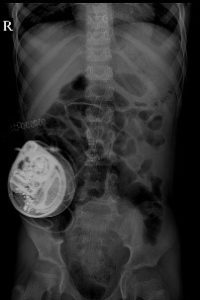
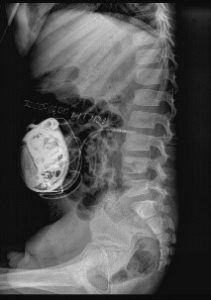
Given below is a picture of the pump (in colour) and X rays of a patients after surgery showing the pump.